

Question to ponder! If dilute sulphuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ) is used instead of dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) for reaction with the metals. K > Na > Ca > Mg > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu > Ag Increasing reactivity Decreasing reactivity Using Experimental Observations Reactivity of Metals Apparatus Hydrogen gas Glass wool soaked in water Metal Heat Heat Water Water Aqueous Potassium hydroxide Hydrogen gas Violent reaction Testing of hydrogen gas: Lighted splint goes off with a ‘pop’ sound Potassium Test for hydrogen gas “ POP”
Apparatus Hydrogen gas Cold water Filter funnel Metal MOST REACTIVE METAL P lease S end C ats M onkeys A nd Z ebras I n L arge H ired C ages M ake S ure P roperly G uarded Potassium (K) Sodium (Na) Calcium (Ca) Magnesium (Mg) Aluminium (Al) Zinc (Zn) Iron (Fe) Lead (Pb) (Hydrogen) Copper (Cu) Mercury (Hg) Silver (Ag) Platinum (Pt) Gold (Au) R E A C T I V I T Y LEAST REACTIVE METAL
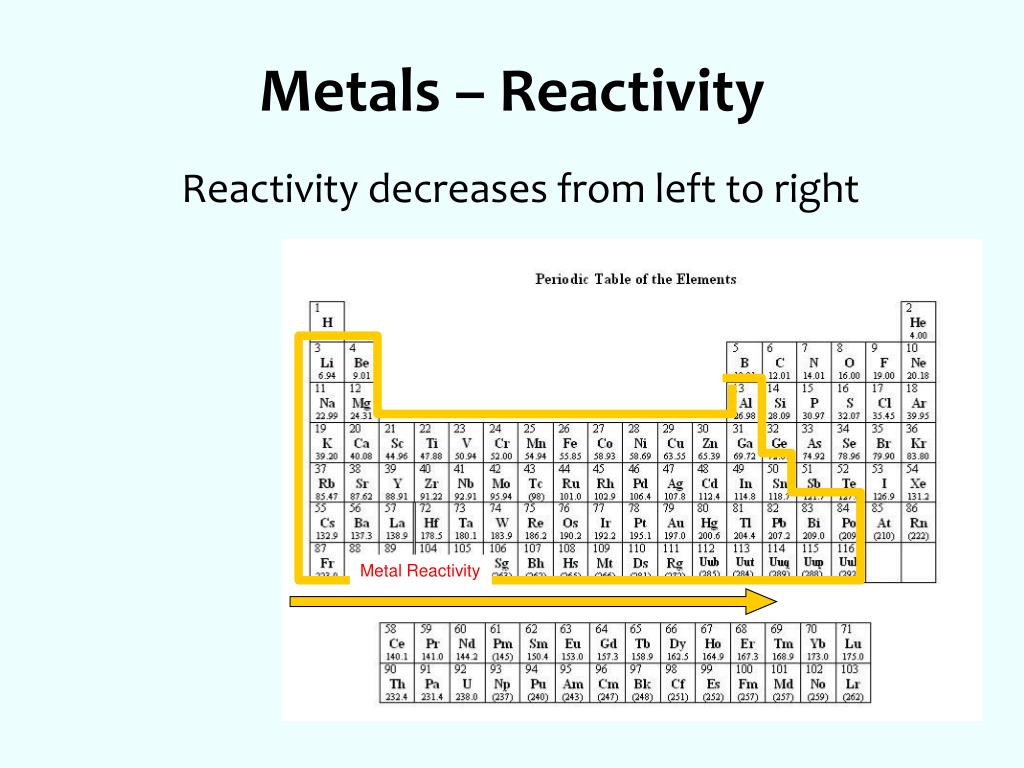
Metal reactivity table series#
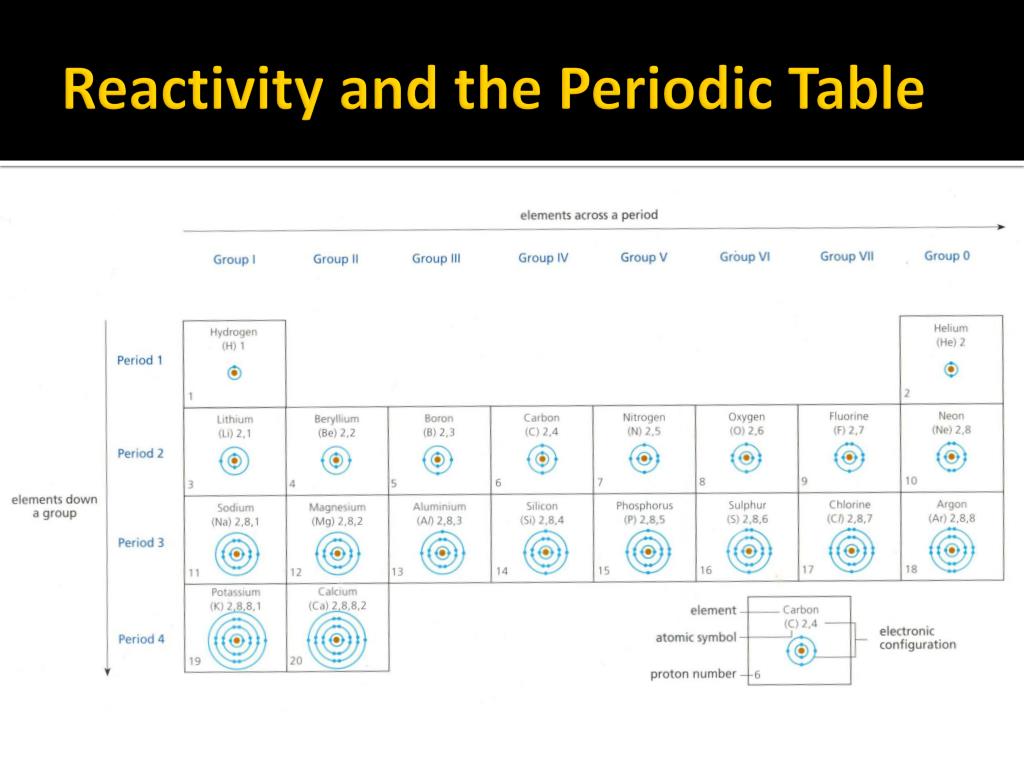
R E A C T I V I T Y MOST REACTIVE METAL LEAST REACTIVE METAL Potassium (K) Sodium (Na) Calcium (Ca) Magnesium (Mg) Zinc (Zn) Iron (Fe) Lead (Pb) (Hydrogen) Copper (Cu) Silver (Ag) P lease S end C ats M onkeys Z ebras I nto L ovely H appy C ages S oon Non-metal Reactivity Series Metals I II III IV V VI VII O 11 Fe 26 Cu Zn 30 29 Ag 47 Na 11 Mg 12 K 19 Ca 20 Pb 82 H 1 METALS CHEMICAL PROPERTIES PHYSICAL PROPERTIES have REACTIVITY OF METALS includes REACTIVITY SERIES Arranged in Most reactive Least reactive Dilute acids Cold water Steam Determined by the reaction Discussed in last lesson Reduction of metal oxides Decomposition of metal carbonates An Overview Chapter 9:METALS METALS: The Reactivity Series Physical properties of metals METALS Solid state at room temp Shiny appearance High density Good heat conductors Good conductors of electricity High Melting and Boiling point Ductile and malleable Strong and tough Except Mercury (Liquid) Due to strong forces (metallic) except Mercury and alkali metals Due to the presence of mobile ions Can be bent and stretched without breaking Atoms are closely packed Due to the presence of mobile ions
Last Lesson… METALS: The Physical Properties of Metals We can therefore confirm their order of reactivity (from most reactive to least) as: potassium, magnesium then zinc. We’d expect the potassium to react explosively (in reality you would never do this in a school laboratory as it is too dangerous), while the magnesium would bubble vigorously and the zinc would form bubbles very slowly.

Rubidium is the second most reactive metal and is very soft, with a silvery-white lustre. Let’s say we carry out the experiment described above by adding potassium, magnesium and zinc into test tubes containing dilute sulfuric acid. Second, the dual criteria of biodegradability and biocompatibility are proposed for BMs, and all metallic elements in the periodic table with accessible data. Rubidium (Rb), chemical element of Group 1 (Ia) in the periodic table, the alkali metal group. The Reactivity of Alkali Metals Explained (animation). The faster the bubbles are given off, the faster the rate of reaction and the more reactive the metal. Table > 4.2 The Reactivity of Alkali Metals Explained (animation). The bubbles are hydrogen gas and can be confirmed using a lit splint, which will produce a ‘squeaky pop’ when the hydrogen burns. It is important that each metal has the same surface area because this will affect the rate of reaction.Ĭount the number of bubbles produced in a given time. Add equal volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid into a series of test tubes then add a equal mass of metal to each test tube.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
